Pricing is one of the most complex yet impactful decisions a small business must make. Finding the optimum price point to drive profitability while resonating with your target customers is crucial yet challenging.
This article explores pricing fundamentals, proven frameworks, innovative models, and actionable tips to equip small business owners with the knowledge to make informed pricing decisions that fuel growth.
Key Takeaways
With the right pricing strategy powered by customer insight, small businesses can unlock substantial profit potential while delivering differentiated value. Remember to:
- Continuously test pricing sensitivity to find optimum balance between profit margins and demand.
- Blend pricing models and promotions to appeal to diverse customer preferences.
- Keep pace with pricing innovation to leverage emerging technologies on the horizon.
The pricing sweet spot maximizing value creation lives at the intersection of customer demand, production costs, and intelligent experimentation. Invest time upfront to determine pricing aligned to business objectives, then stay nimble adapting to ever-changing market landscapes.
Table of Contents
Why Pricing Matters
Before diving into specific pricing techniques, it’s vital to understand why pricing is so critical for small businesses.
Pricing impacts perceptions. The price you set signals the type and level of value your product or service offers. Customers often associate higher prices with higher quality.
Pricing drives profit margins. The price you charge, weighed against costs and expenses, determines your profit potential and sustainability. Even minor price adjustments can massively impact margins.
Pricing influences demand. If your prices are too low, you fail to maximize profit from willing buyers. If prices are too high, you risk pricing out potential customers and losing market share.
With pricing playing such a pivotal role, optimizing your pricing strategy is imperative for commercial success as a small business.
Core Pricing Strategies
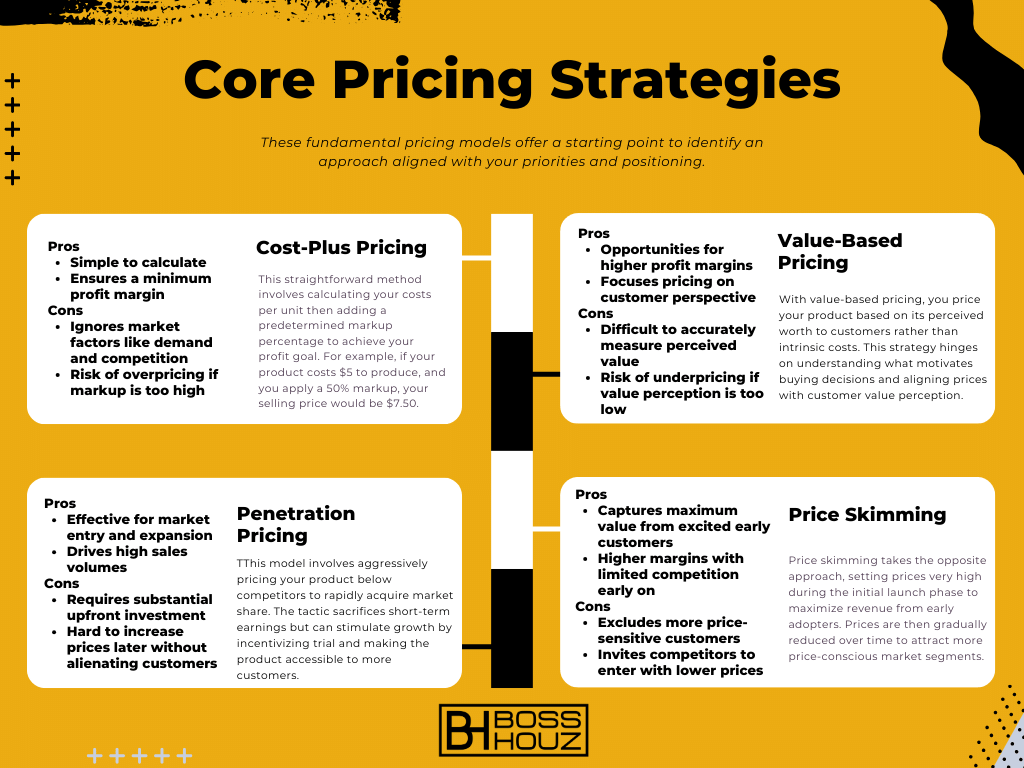
These fundamental pricing models offer a starting point to identify an approach aligned with your priorities and positioning.
Cost-Plus Pricing
This straightforward method involves calculating your costs per unit then adding a predetermined markup percentage to achieve your profit goal. For example, if your product costs $5 to produce, and you apply a 50% markup, your selling price would be $7.50.
Pros
- Simple to calculate
- Ensures a minimum profit margin
Cons
- Ignores market factors like demand and competition
- Risk of overpricing if markup is too high
Cost-plus pricing provides a consistent, low-risk approach for businesses with predictable cost structures. Use it to establish a pricing floor, then validate if the market supports those prices.
Value-Based Pricing
With value-based pricing, you price your product based on its perceived worth to customers rather than intrinsic costs. This strategy hinges on understanding what motivates buying decisions and aligning prices with customer value perception.
Pros
- Opportunities for higher profit margins
- Focuses pricing on customer perspective
Cons
- Difficult to accurately measure perceived value
- Risk of underpricing if value perception is too low
Get insight into value perception by directly surveying customers on pricing thresholds or analyzing the positioning of competitive products. Match prices to the value offered while still maintaining profitability.
Penetration Pricing

This model involves aggressively pricing your product below competitors to rapidly acquire market share. The tactic sacrifices short-term earnings but can stimulate growth by incentivizing trial and making the product accessible to more customers.
Pros
- Effective for market entry and expansion
- Drives high sales volumes
Cons
- Requires substantial upfront investment
- Hard to increase prices later without alienating customers
Penetration pricing is suitable for startups launching disruptive products or services aiming to displace entrenched incumbents. Be prepared to subsidize initial operating losses to gain footing.
Price Skimming
Price skimming takes the opposite approach, setting prices very high during the initial launch phase to maximize revenue from early adopters. Prices are then gradually reduced over time to attract more price-conscious market segments.
Pros
- Captures maximum value from excited early customers
- Higher margins with limited competition early on
Cons
- Excludes more price-sensitive customers
- Invites competitors to enter with lower prices
This model makes sense for innovative products with high demand and little direct competition. Be prepared to lower prices in a structured way as market dynamics shift post-launch.
Innovative Pricing Models
Leverage these advanced frameworks popularized by digital-first brands to unlock additional pricing flexibility and value capture.
Dynamic Pricing
This data-led approach involves continuously modifying prices in response to market demand fluctuations and competitive activity. Enabled by technology, it’s ideal for inventory-constrained businesses like hotels, airlines, and ridesharing platforms.
Pros
- Maximizes revenue by aligning supply and demand
- Responds quickly to changes in the market
Cons
- Can frustrate customers used to fixed prices
- Requires complex software and analysis
While dynamic pricing carries some reputation risk, the revenue upside often outweighs potential customer dissatisfaction. Use carefully and communicate the value customers receive in exchange for variable prices.
Pro Tip: Many ecommerce platforms now provide dynamic pricing tools out-of-the-box!
Psychological Pricing
Psychological pricing leverages consumer behavior quirks to make offerings more enticing. This includes tactics like:
- Charm pricing – pricing just under round numbers ($9.99 instead of $10)
- Anchor pricing – introducing higher-priced products to make target items seem like a relative bargain
Pros
- Drives perception of increased value
- Boosts purchase intent and sales conversion
Cons
- Overuse can damage brand integrity
- Requires deep consumer insight to execute effectively
Sprinkling psychological pricing into your strategy prompts more impulse purchases and positive product perceptions. Just take care not to manipulate customer trust or oversimplify buying motivations.
Freemium Pricing
Under this model, a basic version of a software, app, or service is provided for free, while more advanced capabilities come at a premium cost. The free tier serves to capture a wide user base, upsell premium add-ons, and hook customers into sticky subscriptions.
Pros
- Low barrier to user acquisition
- Built-in upsell opportunities
- Recurring subscription revenue
Cons
- Difficult to convert free users into paying customers
- Heavy reliance on venture capital funding early on
Freemium can be highly effective for digital products with marginal distribution costs per additional user. Focus relentlessly on demonstrating value to transition free users rather than monetizing all users lightly.
Executing a Pricing Strategy
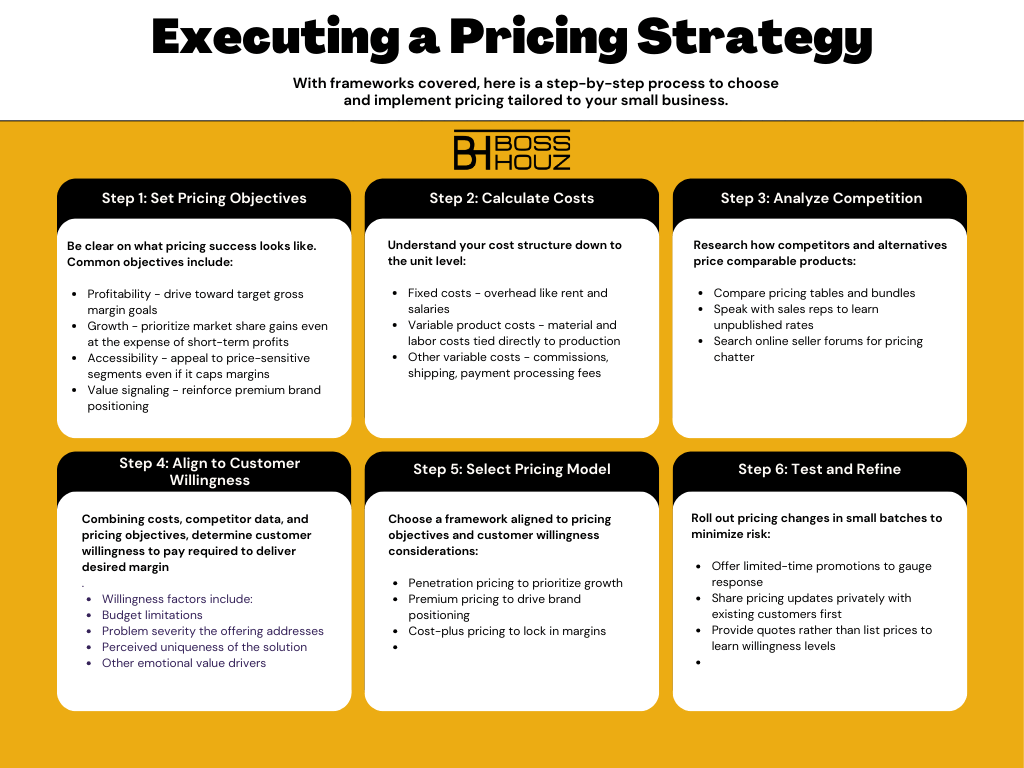
With frameworks covered, here is a step-by-step process to choose and implement pricing tailored to your small business.
Step 1: Set Pricing Objectives
Be clear on what pricing success looks like. Common objectives include:
- Profitability – drive toward target gross margin goals
- Growth – prioritize market share gains even at the expense of short-term profits
- Accessibility – appeal to price-sensitive segments even if it caps margins
- Value signaling – reinforce premium brand positioning
There’s no one right goal—decide what matters most right now.
Step 2: Calculate Costs
Understand your cost structure down to the unit level:
- Fixed costs – overhead like rent and salaries
- Variable product costs – material and labor costs tied directly to production
- Other variable costs – commissions, shipping, payment processing fees
Map expenses at scale to determine break even points and profitability at different volumes.
Step 3: Analyze Competition
Research how competitors and alternatives price comparable products:
- Compare pricing tables and bundles
- Speak with sales reps to learn unpublished rates
- Search online seller forums for pricing chatter
Identify prevailing price thresholds and where competitors hold pricing power or exhibit weaknesses.
Step 4: Align to Customer Willingness
Combining costs, competitor data, and pricing objectives, determine customer willingness to pay required to deliver desired margin.
Willingness factors include:
- Budget limitations
- Problem severity the offering addresses
- Perceived uniqueness of the solution
- Other emotional value drivers
Bridge from costs and competitors to what customers can actually bear.
Step 5: Select Pricing Model
Choose a framework aligned to pricing objectives and customer willingness considerations:
- Penetration pricing to prioritize growth
- Premium pricing to drive brand positioning
- Cost-plus pricing to lock in margins
Get creative blending models across customer segments, purchase volume tiers, or trial offers.
Step 6: Test and Refine
Roll out pricing changes in small batches to minimize risk:
- Offer limited-time promotions to gauge response
- Share pricing updates privately with existing customers first
- Provide quotes rather than list prices to learn willingness levels
Solicit feedback, monitor sales momentum at new prices, and adjust or rollback rapidly based on data.
Pricing Innovation on the Horizon
Pricing strategy continues to grow in sophistication, buoyed by enabling technologies. Here are exciting developments likely to shape pricing over the next 5 years.
AI-Based Price Optimization
Look for machine learning algorithms to crunch market data and simulate demand at different price points with increasing accuracy. Small businesses will leverage AI tools to continuously price optimize based on signals like inventory levels, web traffic, and competitor actions.
Flexible Subscription Plans
Subscription pricing is accelerating across products and services. We’ll see sellers move beyond fixed recurring plans to offer flexible subscriptions with prices adjusting based on usage or access needs over time. Personalization will enable small businesses to tailor pricing to align value.
Decentralized Pricing Networks
Blockchain-based networks will allow buyers and sellers to exchange pricing information and determine real-time market clearing prices without centralized intermediaries. Small vendors can capitalize on transparent demand signals to dynamically price orders across decentralized supply chains and global markets.
Wrapping Up Pricing Strategy
Determining pricing strategy requires thoughtful analysis of internal costs and capabilities, customer demand signals, competitive forces, and alignment to overarching business goals. While the array of frameworks and innovations covered here may seem overwhelming at first, finding the right pricing mix for your small business is very achievable.
Start by identifying your pricing objectives, whether that be profit maximization, growth through accessibility, or premium brand building. Use this desired outcome to guide your framework selection and implementation tactics. Monitor performance closely as you roll out new pricing, soliciting customer feedback and tracking sales momentum. Refine based on data insights rather than gut reactions or assumptions.
If pricing feels intimidating, start small. Perfect your pricing strategy with a pilot product line before scaling more broadly. Seek outside expertise whether through advisors or online learning resources to augment internal capabilities. Proper pricing is challenging yet rewarding work. With the right foundations now in place, the only step left is to get started!








