The rapid pace of technological and economic change is transforming the very nature of work. As artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and automation disrupt traditional business models, entrepreneurs and small businesses must continuously adapt to remain competitive. More than ever, success hinges on the ability to anticipate emerging opportunities and navigate market shifts.
This is spurring growing attention on reskilling and upskilling initiatives to help entrepreneurs and small business workforces prepare for the future of work. Reskilling involves learning new skills to take on different roles, while upskilling focuses on building upon existing capabilities.
Approached strategically, reskilling and upskilling can enable entrepreneurs to identify promising new markets, leverage data and technology to enhance operations, and create innovative customer experiences.
For small businesses, these efforts are crucial to attract and retain talent, boost productivity, and carve out a sustainable niche amid larger competitors.
However, for resource-constrained entrepreneurs and small enterprises, finding the time, funding and direction for effective reskilling and upskilling can prove challenging.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Reskilling and upskilling are essential for entrepreneurs and small businesses to adapt to the future of work.
- Focus is needed on both technical skills as well as “soft” skills like problem-solving and communication.
- Online learning platforms and community partnerships can make training more accessible.
- Progress should be continually measured to ensure effectiveness.
- Reskilling/upskilling and gaining experiential knowledge should go hand-in-hand.
Why Reskill and Upskill? Navigating the Changing Nature of Work
The world of work is evolving rapidly. OECD research finds that 14% of jobs across developed countries face a “high risk” of automation over the next 15 years. Where as the IMF says 40%! Check out my video below:
While some roles may disappear, new ones will also emerge. The 2022 World Economic Forum Future of Jobs report estimates that 97 million new roles may surface across data, AI, engineering, cloud computing, and green economy.
However, 60% of employers surveyed also indicate shortages of skilled talent to fill crucial positions. Developing the Right Skills Can Help Entrepreneurs Seize Opportunities in the Post-COVID World, focusing on areas like digital marketing, data-driven decision making and quality management.
“The future of work requires a new set of skills. Reskilling and upskilling is crucial for anyone pursuing entrepreneurship or building a small business in the years ahead,” said Marc Thompson, Founder of The Entrepreneurial Way.
Beyond technical expertise, the ability to continuously learn, adapt to change and creatively problem-solve will be at a premium.
With speed of change outpacing traditional education pathways, resourceful lifelong learning is imperative for entrepreneurs and small businesses hoping to remain competitive.
Challenges Facing Entrepreneurs and Small Businesses


For entrepreneurs and small business owners, finding direction, time and funding for reskilling and upskilling can prove uniquely challenging:
- Identifying Gaps: Unlike large corporations, most small businesses lack dedicated HR departments to identify reskilling/upskilling requirements and implement training programs.
- Funding Constraints: Smaller training budgets can limit access to learning opportunities, particularly when taking time away from operating the business.
- Lack of Support Infrastructure: From instructors to tools to communities of practice, critical support infrastructure may be lacking for entrepreneurs and small business employees compared to those in larger enterprises.
- Measuring ROI:
“The irony is that those who most need to reskill and upskill often have the hardest time doing so,” said Jane Park, HR advisor. “Entrepreneurs and small businesses must leverage partnerships and technology to enhance access despite limited resources.”
Why Invest in Talent? Benefits for Entrepreneurs and Small Businesses
Despite hurdles, prioritizing and budgeting for reskilling and upskilling delivers significant advantages:
- Competitiveness: Continual learning ensures the workforce has skills aligned to new market realities, keeping the business responsive and able to carve out niche opportunities.
- Innovation: Fresh perspectives and new competencies inspire novel solutions and offerings to capture emerging consumer demands.
- Productivity: Data-driven McKinsey research shows reskilling programs can achieve productivity gains 15-30% higher than traditional hiring.
- Retention: Demonstrating investment in talent makes employees 4.2x more likely to commit long-term, reducing turnover costs.
- Morale: Employees see professional growth opportunities as a major driver of job satisfaction and engagement according to Forbes survey data.
“My philosophy is that if you take care of your employees and show you’re willing to invest in their growth, they’ll do the same for you in return,” said Tabitha Watson, Founder of AllNatural Textiles Co.
Technical Skills to Target
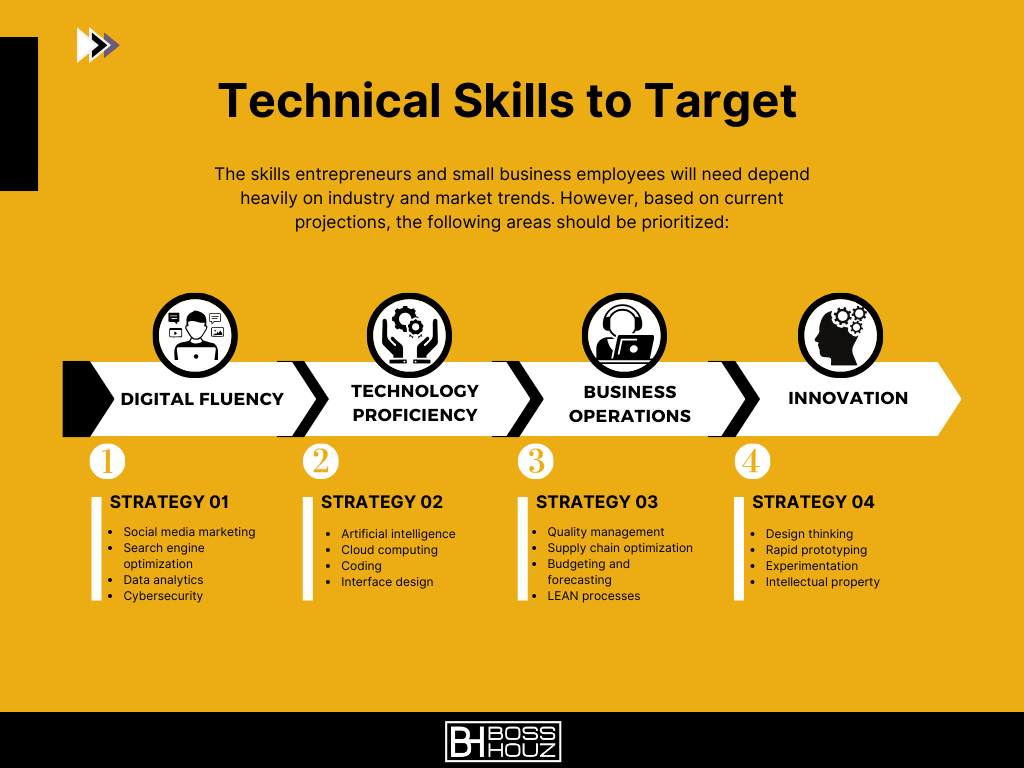

The skills entrepreneurs and small business employees will need depend heavily on industry and market trends. However, based on current projections, the following areas should be prioritized:
Digital Fluency
- Social media marketing
- Search engine optimization
- Data analytics
- Cybersecurity
Technology Proficiency
- Artificial intelligence
- Cloud computing
- Coding
- Interface design
Business Operations
- Quality management
- Supply chain optimization
- Budgeting and forecasting
- LEAN processes
Innovation
- Design thinking
- Rapid prototyping
- Experimentation
- Intellectual property
Soft Skills Critical For Success
While technical skills open opportunities for leveraging emerging tech and trends, human skills remain equally vital for entrepreneurial success.
According to LinkedIn data, creativity, persuasion, collaboration, adaptability and time management represent the top soft skills required by companies.
Customer Focus & Empathy
- User experience design
- Interviewing & surveying
- Cultural & regional awareness
Leadership & Management
- Motivating & developing teams
- Cross-functional collaboration
- Coaching & mentoring
Problem Solving & Resilience
- Conflict resolution
- Critical thinking
- Risk assessment
- Managing ambiguity
Mastering this mix of technical and soft skills enables entrepreneurs to seamlessly navigate external opportunities and internal organizational needs for sustained growth.


Cost-Effective Reskilling & Upskilling Strategies
Accessing quality reskilling and upskilling development need not require big budgets. Entrepreneurs and small businesses can utilize the following approaches:
Online Learning Platforms
Platforms like Udacity, Coursera and edX offer highly affordable courses in specialized technical skills. Microdegrees provide deep capability building for emerging competency areas.
Automated Assessments
Tools like Pymetrics and Kenjo leverage AI algorithms and gaming simulations to evaluate strengths, and customize learning pathways aligned to individuals’ talents.
Mobile Learning
Bite-sized daily learning through well-designed apps allows entrepreneurs and employees to continually upskill during pockets of downtime.
Gamified Learning
Online simulations, real-world challenges, badge incentives and leaderboards turns skill-building into an engaging, addicting experience.
Government Initiatives
State and national government programs offer grants, tax benefits and partnerships to help entrepreneurs and small businesses fund training initiatives.
Local Community Partnerships
Community colleges, libraries, Small Business Development Centers and nonprofits are valuable—and often free—local resources for training.
Measuring Training Impact
While accessing training has become easier, evaluating effectiveness remains imperative. Some frameworks and metrics to drive value include:
- Skills audits comparing capabilities before and 3-6 months post-training
- Benchmarks for productivity and innovation quarterly and annually
- Profitability targets specifically tied to reskilling/upskilling initiatives
- Growth goals for expansion into new markets based on new expertise
- Retention metrics to track employee turnover rate changes
Tying learning programs directly to key performance indicators through frameworks like the Kirkpatrick Model can clarify the ROI on reskilling and upskilling investments.
Key Focus Areas Aligned to Work Trends
While foundational business and technological skills will always remain essential, trends reshaping work are creating new demands for specific future-focused expertise:
Sustainable Business Models
Consumer demand has made business ethics and environmental sustainability competitive differentiators. Reskilling/upskilling areas like:
- Circular supply chains
- Carbon accounting
- Green products/services
- ESG reporting
Data-Enhanced Offerings
Data analytics and personalized experiences enabled by AI are becoming fundamental for all enterprises. Important skills include:
- Predictive analytics
- Visualization platforms
- Customer analytics
- Machine learning application
Direct-to-Consumer Approaches
Direct-to-consumer (D2C) e-commerce brands are creating new competition. Key skills to develop:
- Social commerce
- Performance marketing
- CX optimization
- Fulfillment/logistics
Hybrid Work Models
“Work from anywhere” policies demand new ways of coordinating, engaging employees and supporting well-being:
- Virtual teambuilding
- Asynchronous communication
- Workplace wellness
- Collaborative platforms
Continuous learning around emerging and evolving workplace practices ensures entrepreneurs remain responsive in the years ahead.
Experiential Learning Essential for Entrepreneurs
While courses and credentials are valuable, entrepreneurship inherently demands learning by doing. Sites like Meetup offer local groups and events to connect directly with experienced founders across various industries for real insights.
Incubators, accelerators and shared workspaces also provide built-in communities of entrepreneurs at all stages open to sharing expertise and advice.
Actively networking at industry events and trade shows generates opportunities to meet recognized leaders. Volunteering through programs like SCORE that provide free mentorship to entrepreneurs can further enhance visibility.
Hands-on learning experiences like hackathons to rapidly build out ideas, coworking hosting programs to directly work with customers and companies, and business plan competitions to test theories are also invaluable to refine entrepreneurial skills and thinking.
Lifelong Learning Essential to Navigate Work Evolution
The half-life of professional skills continues to decline. Technical skills now have an average lifespan around 2.5-5 years according to Deloitte. To remain competitive, entrepreneurs and small businesses must continually reskill and upskill.
Leveraging lower-cost online learning options, strategic partnerships, hands-on experiences and ongoing progress tracking allows even resource-constrained organizations to ensure their people keep pace.
While the future of work remains unpredictable, a culture embracing growth, adaptability and new possibilities will best position any entrepreneur for ongoing success in times of unprecedented change.








